雲計算
出自 MBA智库百科(https://wiki.mbalib.com/)
雲計算(cloud computing,臺灣譯作雲端運算)
雲計算(cloud computing,臺灣譯作雲端運算),是分散式計算技術的一種,其最基本的概念,是透過網路將龐大的計算處理程式自動分拆成無數個較小的子程式,再交由多部伺服器所組成的龐大系統經搜尋、計算分析之後將處理結果回傳給用戶。透過這項技術,網路服務提供者可以在數秒之內,達成處理數以千萬計甚至億計的信息,達到和“超級電腦”同樣強大效能的網路服務。
雲計算是一種資源交付和使用模式,指通過網路獲得應用所需的資源(硬體、平臺、軟體)。提供資源的網路被稱為“雲”。“雲”中的資源在使用者看來是可以無限擴展的,並且可以隨時獲取。這種特性經常被比喻為像水電一樣使用硬體資源,按需購買和使用。[1](Cloud computing is a resource delivery and usage model, it means get resource (Hardware, software)via network. The network of providing resource is called ‘Cloud’. The hardware resource in the ‘Cloud’ seems scalable infinitely and can be used whenever.)[2]
最簡單的雲計算技術在網路服務中已經隨處可見,例如搜尋引擎、網路信箱等,使用者只要輸入簡單指令即能得到大量信息。
未來如手機、GPS等行動裝置都可以透過雲計算技術,發展出更多的應用服務。
進一步的雲計算不僅只做資料搜尋、分析的功能,更可計算一些像是分析DNA結構、基因圖譜定序、解析癌症細胞等。
稍早之前的大規模分散式計算技術即為“雲計算”的概念起源[1]。
Google目前的雲技術,主要由MapReduce、GFS及BigTable三項所組成
雲是指網際網路,因過去一直將網際網路畫成一朵雲。
雲計算如何實現隨用隨取[3]
隨著雲計算的不斷成熟,越來越多的用戶嘗試用“雲”來解決傳統線下場景存在的難題;數以萬計的中小企業創業者,更是在數字化轉型的關口,搭上了發往“雲上”的“高速列車”。
從某種意義上,雲計算已經成為像水、電一樣重要的基礎資源。只要到雲服務平臺註冊一個賬號,企業和個人用戶就可以通過互聯網方便快捷地獲取所需的IT資源和技術能力,既降低成本,又滿足靈活部署、高效率的業務需求。隨著數字化、智能化轉型深入推進,雲計算正扮演著越來越重要的角色。
2019年“雙11”購物節,一過零點,各大電商平臺即迎來交易高峰。零點剛過1分36秒,天貓平臺上成交總額突破100億元,訂單創建峰值更是創下新的世界紀錄——1秒鐘內有54.4萬筆訂單同時下單,是2009年第一次“雙11”的1360倍。成功扛住全球最大規模流量“洪峰”、支撐各大電商平臺“雙11”購物盛況的,正是背後的阿裡雲、騰訊雲等各大雲計算服務平臺。
兩個月前,阿裡巴巴悄悄完成了浩大的遷徙工程,將數以十萬計的物理伺服器從線下數據中心遷移到了“雲上”。但淘寶、天貓的消費者和商家對這個“給飛機換引擎”的過程毫無感知。
“雲計算是一種IT資源和技術能力的共用。在傳統模式中,個人開發者和企業需要購買自己的硬體和軟體系統,還需要運營和維護。”騰訊公司副總裁、騰訊雲總裁邱躍鵬說,有了雲計算,用戶可以不用去關心機房建設、機器運行維護、資料庫等IT資源建設,而可以結合自身需要,靈活地獲得對應的雲計算整體解決方案。這些解決方案,目前廣泛應用在互聯網、金融、零售、政務、醫療、教育、文旅、出行、工業、能源等各個行業。
可以說,雲計算是IT產業水到渠成的產物:計算量越來越大,數據越來越多、越來越動態、越來越實時,雲計算於是應運而生。正因如此,阿裡巴巴、騰訊、華為等行業領先企業在滿足自身需求後,又將這種軟硬體能力提供給有需要的其他企業。
目前,雲計算已被廣泛應用到各個領域,併發揮了巨大作用。阿裡巴巴集團副總裁劉松介紹說,雲平臺的成本、安全和管理集約優勢,可以降低IT架構和系統構建的成本。目前,國內大多數互聯網應用構建在雲平臺上。
雲服務可以按需提供彈性的IT服務。用戶可以根據自身需要調配IT資源,在保障應用需求的同時節約成本。比如,鐵路12306系統就使用阿裡雲平臺支撐春運等購票峰值的IT需求,保障系統在高峰期的穩定運行。
另一方面,雲計算也成為城市、政府和各行業數字化轉型的基礎支撐。當前無論是電商平臺,還是網上外賣平臺、線上游戲中心、熱點網站,或是工業互聯網,都離不開雲計算。近年來,政府部門開始積極利用雲計算技術提升工作效率和服務水平,中國政務服務小程式就是一個典型案例:它接入了各部門、各地方的142萬項政務服務指南。用戶只需打開微信登錄小程式,動動手指即可辦理從前需要跨部門、跨地區甚至跨省市事項。它依托的,就是騰訊雲計算技術構建的數據共用政務雲平臺。
最新的數據顯示,2019年全球雲上的IT基礎設施占比超過了傳統數據中心,成為市場主導者。這反映出,“企業上雲”已完成從被動到主動的轉變。
雲計算技術的普及,讓人工智慧這樣需要海量數據和大規模投入的前沿科技不再高不可攀。基於雲計算平臺使用人工智慧,能極大降低成本,為各行各業最大程度應用人工智慧技術提供可能。
與此同時,大數據、物聯網、人工智慧、5G技術的成熟與普及,也加速著雲計算的技術演進,並促進雲計算市場快速發展。劉松介紹,雲平臺是大數據、物聯網、人工智慧、5G這些新的技術應用的基礎,隨著新技術的普及,對雲平臺的技術和服務能力必然提出更高的要求,如更大的算力支撐、有力的安全保障。
專家表示,融合是新一代網路信息技術的重要特征。雲計算、大數據、物聯網、人工智慧、5G這些技術只有相互配合,才能真正發揮作用。例如,物聯網產生海量數據,5G用來傳輸和交換,而數據存儲與計算需要雲平臺作為承載,人工智慧也需要雲平臺提供算力和數據支持。其中,“5G+雲+人工智慧”的組合最具代表性,三者緊密融合,釋放出巨大能量,進一步推動“智能製造”“智能網聯車”“智慧城市”等產業的發展。
當然,對雲計算來說,在與其他新技術融合同時也面對挑戰。專家指出,5G最先落地也是用戶體驗最直接的場景,將是大帶寬的應用,所產生的海量連接、規模效應將對雲平臺造成很大衝擊。邱躍鵬認為,只有跨越了規模效應的門檻後,雲計算才能更好地把技術創新轉化為產品創新,並提供產業升級的整體解決方案。
他說,隨著雲計算承載的業務規模越來越大,軟體和硬體的結合成為剛需,用軟硬體一體化技術搭建出更強壯的基礎設施平臺,會成為雲計算發展的重要趨勢。
專家指出,作為向數字化、智能化轉型的重要基礎設施,我國雲計算產業已進入發展的關鍵階段,需要進一步推動雲計算、5G等信息基礎設施建設,讓雲計算服務的門檻越來越低,真正可以像水和電一樣去使用。
2019年10月發佈的《中國雲計算產業發展與應用白皮書》(下稱《白皮書》)預測,到2023年我國政府和企業上雲率將超過60%。《白皮書》同時指出,影響雲計算產業發展和應用的最普遍、最核心的制約因素,就是雲計算的安全性和數據私密性保護。雲上數據安全已成為業務數字化、智能化升級的關鍵風險點。
“雲計算的每一次發展與擴大,都是對雲安全的一次壓力與挑戰。”劉松說,大量的企業雖然上雲了,但對安全的理解以及準備仍然不足。雲計算安全也已不再是單點安全,而是與全球產業鏈各個環節息息相關,原始的安全架構與能力已無法抵禦全球化的網路安全威脅。
專家指出,在業內,雲安全發展水平目前落後於雲計算發展約4年,儘管雲平臺的安全性已有相當保障,但仍存在不少挑戰。
由於雲平臺接入了大量網路應用和企業服務,一旦出現故障,影響範圍甚廣,會導致眾多網站無法訪問、手機APP不能使用。隨著企業上雲和數字化轉型升級的不斷深化,數據泄露已發展成為全球最常見的安全問題。根據相關安全機構統計,僅2019年上半年,全球範圍內就發生了3813起數據泄露事件,被公開數據為41億條,其中8起安全事件就導致了32億條的數據泄露。
騰訊安全雲鼎實驗室負責人董志強介紹說,除了數據安全,雲安全還面臨網路黑產不法團夥的侵入。隨著越來越多的企業上雲,瞄準雲上的企業發動攻擊的犯罪團夥也越來越多。與以往的單兵作戰不同,網路黑產團夥日益公司化、鏈條化和智能化,“羊毛黨”“黃牛黨”“拒絕服務攻擊”“流量劫持”等對整個雲計算產業發展造成了巨大威脅。因此,為進一步提升雲平臺的安全性能,騰訊也聯合相關機構舉辦基於真實雲環境的安全挑戰賽,在真實環境中進行攻防研究。
“雲計算的大規模應用,對安全能力的要求一定會成倍增長。但同時也可以看到,雲計算、智能化給安全帶來了新的契機,也會讓更多企業感受到雲原生安全帶來的利好。”劉松說。相比於傳統的修補式的IT安全,雲安全其實更具優勢,是目前最有可能實現原生安全即“內嵌”安全的。這種原生安全,不會隨著雲計算規模的擴大風險更高,規模的擴大反而有助於降低雲安全的部署成本。
邱躍鵬認為,為了早日實現“原生安全”的目標,將安全真正“內嵌”到雲服務當中,雲服務商應該加快對雲安全前沿技術和基礎安全的研究,保障雲平臺和平臺上用戶的安全。上雲的企業也需要認識到雲的原生安全能力的價值,加強網路安全意識,推動自身安全架構的進化。
專家指出,對雲計算來說,最核心的安全是基礎設施的安全。從國家安全、產業健康可持續發展的角度來看,自主可控的核心技術研發成為我國雲計算產業發展必須要解決的問題。要鼓勵龍頭企業和研究機構開放平臺資源,帶動產業鏈上核心晶元、基礎軟體、應用軟體、關鍵設備、大數據平臺等關鍵環節的發展,堅持自主可控前提下的市場化發展。
雲端儲存(cloud storage)是一種將數據保存在虛擬伺服器上的數據類型,通常意義上,數據存儲在第三方媒介,而非特定單一伺服器上。
2007年10月,Google與IBM開始在美國大學校園,包括卡內基美隆大學、麻省理工學院、史丹佛大學、加州大學柏克萊分校及馬利蘭大學等,推廣雲計算的計劃,這項計劃希望能降低分散式計算技術在學術研究方面的成本,併為這些大學提供相關的軟硬體設備及技術支援(包括數百台個人電腦及BladeCenter與System x伺服器,這些計算平臺將提供1600個處理器,支援包括Linux、Xen、Hadoop等開放源代碼平臺)。而學生則可以透過網路開發各項以大規模計算為基礎的研究計劃[1]。
2008年1月30日,Google宣佈在臺灣啟動“雲計算學術計劃”,將與臺灣大學、臺灣交通大學等學校合作,將這種先進的大規模、快速計算技術推廣到校園[4]。
2008年8月3日,美國專利商標局(以下簡稱“SPTO”)網站信息顯示,戴爾正在申請“雲計算”(Cloud Computing)商標,此舉旨在加強對這一未來可能重塑技術架構的術語的控制權。戴爾在申請文件中稱,雲計算是“在數據中心和巨型規模的計算環境中,為他人提供電腦硬體定製製造”。[5]。
雲計算與IT技術[1]
雲計算是隨著處理器技術、虛擬化技術、分散式存儲技術、寬頻互聯網技術和自動化管理技術的發展而產生的. 這種大規模的計算能力通常是由分散式的大規模集群和伺服器虛擬化軟體搭建。(Cloud computing and technology:New advances in processors, virtualization technology, distributed storage, broadband Internet access , automated management and fast, inexpensive servers have all combined to make cloud computing a compelling paradigm.This vast process power is usually got with a distributed, large-scale server cluster and server virtualization software.)
雲計算使用模式[1]
傳統的計算模式下,單台台式機的資源用來完成任務。在客戶伺服器模式下,伺服器用來執行任務。在雲計算模式下,網路超級電腦—“雲”用來執行任務。用戶能在任何時間任何地點通過互聯網獲取計算、存儲、網路資源,並且能夠按照處理器利用率、存儲使用量、帶寬消耗付費。(Cloud computing usage model:In traditional computing model, tasks are completed using a single desktop computer. In the client/serer model, tasks are completed using a remote server. In cloud computing model, tasks are completed using ‘Cloud’-a network super computer.Cloud computing allows users and companies to pay for and use the services and storage that they need, when they need them and, as wireless broadband connection options grow, where they need them. Customers can be billed based upon server utlilization, processing power used or bandwidth consumed.)
雲計算的影響[1]
雲計算有可能顛覆軟體產業,應用和許可被隨時購買和生效,應用在網路上而不是本機上運行。這種轉變將數據中心放在網路的核心位置,而所有的應用所需要的計算能力、存儲、帶寬、電力都由數據中心提供。雲計算不僅影響商業模式,還影響開發、部署、運行、交付應用的方式。(Cloud computing impact:As a result, cloud computing has the potential to upend the software industry entirely, as applications are purchased, licensed and run over the network instead of a user's desktop. This shift will put data centers and their administrators at the center of the distributed network, as processing power, electricity, bandwidth and storage are all managed remotely. It affects not only business models, but the underlying architecture of how we develop, deploy, run and deliver applications.)[6]
雲計算對服務提供商意味著什麼[1]
- 快速部署(Fast Provision)
- 縮小主機規模(Reduce servers scale)
- 提高資源利用率(Increase resource utilization rate)
- 提高管理效率(Improve management efficiency)
- 降低運維成本(Lower maintenance cost)
- 基礎設施可以放置在低土地和能源成本的地區(Location of infrastructure in areas with lower costs of real estate and electricity)
- 提供商業連續性服務(Provide business continuity service)
- 提高管理效率(Improve management efficiency)
- 提高服務水平(Improve service levels)
- 複雜的體繫結構(Complex architecture)
- 商業模式和理念的轉變(Change of business model and faith)
雲計算對於用戶意味著什麼[1]
- 用戶端負載降低(Lower client workload)
- 降低總體擁有成本(Lower Total Cost Ownership)
- 可能將應用的開發與基礎設施維護相對分離(Separation of infrastructure maintenance duties from domain-specific application development)
- 可能將程式代碼與物理資源分離(Separation of application code from physical resources)
- 不需要為一次性任務或罕見的負載狀況準備大量設備(Not have to purchase assets for one-time or infrequent intensive computing tasks)
- 按需擴展資源(Expand resource on-demand)
- 使應用具有高可用性(Make the application have high availability)
- 快速部署應用(Quickly deploy application)
- 按使用付費(Pay per use)
雲計算基礎設施基本特征[1]
- 自愈合(Self-healing)
- 多用戶使用(Multi-tenancy)
- 虛擬化(Virtualized)
- 線形擴展(Linearly ScalableLinearly Scalable)
- 資源監控和測量(Resource Monitor and measure)
- 資源註冊和發現(Resource registration and discovery)
雲計算的關聯概念[1]
雲計算正成為行業中的熱點概念。它和下麵的辭彙產生了或多或少的關連:網格計算,效用計算,虛擬化,伺服器集群,主機租用,主機托管。雲計算平臺普遍用到了虛擬化技術,並且基於一個集群來構建,和網格計算和效用計算以及SaaS有著天然的聯繫,而且被用在IDC行業與主機租用和主機托管業務競爭。(Cloud computing’s brother buzzwords:Cloud computing is becoming one of the next industry buzz words. And it has more or less relation with these words: grid computing, utility computing, virtualization, server cluster, Dedicated server, Colocation. Cloud computing infrastructure usually use virtualization technology, and is built based on a server cluster, have nature relation to grid computing and utility computing, and is use to compete with Dedicated server and Colocation.)
相對與雲計算的兄弟概念而言,雲計算只是剛剛興起。從Google Trend 獲取的信息我們可以看到,雲計算在2007年末才被該系統統計,並且一直處於上升趨勢。而同時,網格計算、效用計算、分散式計算的概念卻呈現下降趨勢。雲計算和虛擬化應該會在托管平臺上有所作為,而主機租用已經呈現下降趨勢。(Cloud computing break out:Compared to its brother buzzwords, cloud computing is just beginning. Trends in usage of the terms from Google searches shows Cloud Computing is a relatively new term introduced in the past year. There has also been a decline in general interest of Grid, Utility and Distributed computing. Cloud Computing and Virtualization are the next hot hosting platforms; the Dedicated server term is slowly starting to lose ground vs. Virtualization and Cloud Computing.)
效用計算是一種提供計算資源的商業模式,用戶從計算資源供應商獲取和使用計算資源並基於實際使用的資源付費。簡單說,是一種基於資源使用量的付費模式。效用計算主要給用戶帶來經濟效益。企業數據中心的資源利用率普遍在20%左右,這主要是因為超額部署—購買比平均所需資源更多的硬體一邊處理峰值負載,可預計到的或不可預計的。效用計算則允許用戶只為他們所需要用到並且已經用到的那部分資源付費。(Utility computing is a business model of providing computing resource, user get and use the computing resource from service provider and pay for practically used resource. To say it simply, it is a price model based on resource usage quantity. The main benefit of utility computing is better economics. Corporate data centers are notoriously underutilized, with resources such as servers often idle 85 percent of the time. This is due to overprovisioning — buying more hardware than is needed on average in order to handle peaks (such as the opening of the Wall Street trading day or the holiday shopping season), to handle expected future loads and to prepare for unanticipated surges in demand. Utility computing allows companies to only pay for the computing resources they need, when they need them.)
效用計算是是一種分發應用所需資源的計費模式。 雲計算是一種計算模式, 代表了在某種程度上共用資源進行設計、開發、部署、運行應用,以及資源的可擴展收縮和對應用連續性的支持。效用計算通常需要雲計算基礎設施支持,但並不是一定需要。同樣,在雲計算之上可以提供效用計算,也可以不採用效用計算。(Comparison of Utility Computing and Cloud Computing:Utility computing is a business model, it is a type of price model to deliver application infrastructure resource. Cloud computing is a computing model, relates to the way we design, build, deploy and run applications that operate in a sharing resources and boasting the ability to dynamically grow, shrink and self-heal. Utility computing is often need a cloud computing infrastructure, but not must need. Sameness, above the cloud computing, we can adopt utility computing, and, we can adopt other price model.)[7][8][9]
分散式計算是指在一個鬆散或嚴格約束條件下使用一個硬體和軟體系統處理任務,這個系統包含多個處理器單元或存儲單元,多個併發的過程,多個程式。一個程式被分成多個部分,同時在通過網路連接起來的電腦上運行。分散式計算類似於並行計算,但並行計算通常用於指一個程式的多個部分同時運行於某台電腦上的多個處理器上。所以,分散式計算通常必須處理異構環境、多樣化的網路連接、不可預知的網路或電腦錯誤。(Distributed Computing:Distributed computing deals with hardware and software systems containing more than one processing element or storage element, concurrent processes, or multiple programs, running under a loosely or tightly controlled regime.In distributed computing, a program is split up into parts that run simultaneously on multiple computers communicating over a network. Distributed computing is a form of parallel computing, but parallel computing is most commonly used to describe program parts running simultaneously on multiple processors in the same computer. Both types of processing require dividing a program into parts that can run simultaneously, but distributed programs often must deal with heterogeneous environments, network links of varying latencies, and unpredictable failures in the network or the computers.)[10][11]
網格計算是指分散式計算中兩類比較廣泛使用的子類型。一類是,在分散式的計算資源支持下作為服務被提供的線上計算或存儲。另一類是,一個鬆散連接的電腦網路構成的一個虛擬超級電腦,可以用來執行大規模任務。該技術通常被用來通過志願者計算解決計算敏感型的科研、數學、學術問題,也被商業公司用來進行電子商務和網路服務所需的後臺數據處理、經濟預測、地震分析等。(Grid computing:Grid computing is a term for either of two broad subcategories of distributed computing: 1 Online computation or storage offered as a service supported by a pool of distributed computing resources, also known as utility computing, on-demand computing, or cloud computing. Data grids provide controlled sharing and management of large amounts of distributed data, often used in combination with computational grids. 2 The creation of a "virtual supercomputer" composed of a network of loosely-coupled computers, acting in concert to perform very large tasks. This technology has been applied to computationally-intensive scientific, mathematical, and academic problems through volunteer computing, and it is used in commercial enterprises for such diverse applications as drug discovery, economic forecasting, seismic analysis, and back-office data processing in support of e-commerce and web services.[12]
網格計算強調資源共用,任何人都可以做為請求者使用其它節點的資源,任何人都需要貢獻一定資源給其他節點。網格計算強調將工作量轉移到遠程的可用計算資源上。雲計算強調專有,任何人都可以獲取自己的專有資源,並且這些資源是由少數團體提供的,使用者不需要貢獻自己的資源。在雲計算中,計算資源被轉換形式去適應工作負載,它支持網格類型應用,也支持非網格環境,比如運行傳統或Web2.0應用的三層網路架構。
網格計算側重並行的計算集中性需求,並且難以自動擴展。雲計算側重事務性應用,大量的單獨的請求,可以實現自動或半自動的擴展。(Grid computing emphasizes on resource sharing, every grid node can apply for resource from other nodes, and every node should contribute resource to the grid. The focus of grid computing is on the ability of moving a workload to the location of theneeded computing resources, which are mostly remote and are readily available for use.Grids also require applications to conform to the grid software interfaces.Cloud computing emphasize on proprietary, every user out of the cloud can get it’s own private resource from the cloud, and the cloud resource are provided by the specific service provider, the user need not contribute its resource. In a cloud environment, computing resouces, such as servers, can be dynamically shaped or carved out from its underlying hardware infrastructure and made available to a workload. In addition, while a cloud does support grid, a cloud can also support nongrid environments,such as a three-tier Web architecture running traditional or Web 2.0 applications.Grid computing emphasizes on computing sensitive task, and is difficult to automated scale. Cloud computing emphasizes on transactional application, a great amount of separate request, and can scale automatically or semiautomatically.)[13][14][15]
伺服器集群是指將一組伺服器關聯起來,使它們在外界從很多方面看起來如同一臺伺服器。集群內的伺服器之間通常通過區域網連接,通常用來改善性能和可用性,但一般而言比具有同等性能功能和可用性的單台主機具有更低的成本。(Computer cluster:A computer cluster is a group of coupled computers that work together closely so that in many respects they can be viewed as though they are a single computer. The components of a cluster are commonly, but not always, connected to each other through fast local area networks. Clusters are usually deployed to improve performance and/or availability over that provided by a single computer, while typically being much more cost-effective than single computers of comparable speed or availability.[16])
網格通常更加鬆散連接、異構、地理位置分散,主機之間信任度更低。(Grids tend to be more loosely coupled, heterogeneous, and geographically dispersed, grid computers do not fully trust each other.)
虛擬化指對計算資源進行抽象的一個廣義概念。虛擬化對上層應用或用戶隱藏了計算資源的底層屬性。它既包括使單個的資源(比如一個伺服器,一個操作系統,一個應用程式,一個存儲設備)劃分成多個虛擬資源,也包括將多個資源(比如存儲設備或伺服器)整合成一個虛擬資源。虛擬化技術是指實現虛擬化的具體的技術性手段和方法的集合性概念。虛擬化技術根據對象可以分成存儲虛擬化、計算虛擬化、網路虛擬化等。計算虛擬化可以分為操作系統級虛擬化,應用程式級,和虛擬機管理器。虛擬機管理器分為宿主虛擬機和客戶虛擬機。(Virtualization:Virtualization is a broad term that refers to the abstraction of computer resources. Virtualization hides the physical characteristics of computing resources from their users, be they applications, or end users.[16] This includes making a single physical resource (such as a server, an operating system, an application, or storage device) appear to function as multiple virtual resources; it can also include making multiple physical resources (such as storage devices or servers) appear as a single virtual resource.[16] Virtualization technology is a aggregative term of technical means and methods to implement virtualization. It can be divided to many types based on objects: storage virtualization, computing virtualization, network virtualization. Computing virtualization include:OS level virtualization, application level virtualization, hyper visor. Hypervisor include: host vm and guest vm.)
雲計算存在的難題[1]
- 連續高可用性(Continuous high availability)
- 某個集群的失效處理
- 一致性(Consistency)
- 不同集群的同步
- 互操作性和標準化(Interoperability and standarlization)
- 在萌芽和成長期,各廠商都試圖建立自己的介面API
- 所有構件的擴展(Scalability of all components)
- 信息保密(Data secrecy)
- 跨地區存儲和數據傳輸可能會引發法律和政治問題(Legal and political problem of data store and translation across regions)
- 性能問題(Performance issue)
- 差異化定製問題(Difficulty customizing)
- 組織障礙(Organizational obstacle)
雲計算架構[1]
雲計算平臺一般分為以下幾層:物理設施,虛擬化,管理,服務提供。物理設施被虛擬化,提供一個靈活的資源池體提高資源利用率。管理層負責物理資源和虛擬資源池的管理、部署、監控、報警等。服務提供層組合管理層的功能提供某種形式的服務。(he physical hardware layer is virtualized to provide a flexible adaptive platform to improve resource utilization. The keys to new enterprise data center infrastructure services are the next two layers, the virtualization environment and management layer. The combination of these two layers ensure that resources in a data center are efficiently managed and can be provisioned, deployed, and configured rapidly.)
10個使用雲計算服務的企業[1]
1. The NY Times(Amazon EC2)
2. Nasdaq(Amazon S3)
3. Major League Baseball(Joyent)
4. ESPN(Rightscale using Amazon EC2)
5. Hasbro(Amazon EC2)
6. British Telecom(3Tera)
7. Taylor Woodrow(Google Apps)
8. CSS(Amazon EC2)
9. Activision(Amazon EC2)
10. Business Objects (A SAP Company)(Rightscale using Amazon EC2)
雲計算市場劃分和參與者[1]
雲計算技術和方案提供者:
- 3Tera - AppLogic grid OS used as cloud computing platform by service providers and enterprises
- Appistry - Cloud computing middleware - Enables easily scalable cloud computing in the enterprise.
- Cassatt - Cassatt Active Response platform enables administrators to set policies to power physical and virtual servers safely on and off and pool their computing resources.
- CloudScale Networks - Cloud enabler. Currently in private ALPHA only
- CloudHan - Cloud tech and infrastructure consultant, in China.
- Enomaly Inc - Service Provider & Cloud Enabler - Developer of the Enomalism Elastic Computing Platform & Elastic Drive
- Q-layer - provides software for data centers that enables cloud computing, support VSAN, VLAN, VPDC, currently support VMware ESX.
- Skytap - IaaS service optimized for QA, Training, Demo, and Ops Testing. Supports VMware, Xen hypervisors & Windows, Linux & Solaris OS guests.
雲計算基礎設施層服務:
- Agathon Group - Cloud provider. Services include highly available VPS, virtual private datacenters and ready-to-use LAMP stacks. Self-service ordering. Custom development and managed services available.
- Amazon Web Services - Amazon EC2/S3 (Hardware-a-a-S & Cloud Storage)
- CohesiveFT - CohesiveFT Elastic Server On-Demand
- ElasticHosts - UK-based instant, on-demand servers in the cloud
- Flexiscale - Another instant provisioner of web servers with some advanced features like auto-scaling coming soon.
- GoGrid - instant, on-demand servers offering "control in the cloud". Deploy Windows/Linux servers via web-interface in minutes
- GridLayer - Cloud Provider. A service by Layered Technologies that delivers Virtual Private Datacenters and virtual private servers from grids of commodity servers
- LayeredTechnologies - Cloud Provider. provider of on-demand hosting and cloud and utility computing solutions through its brand GridLayer
- Mosso - Rackspace's cloud hosting service
- Newservers - Instant provisioning of web servers either Windows or Linux
雲計算平臺層服務:
- Bungee Connect - Provides end to end tools and systems required to develop, deploy and host web applications (Platform as a Service)
- Coherence - Oracle Coherence Data Grid for EC2 and other cloud platforms
- Force.com - Salesforce.com's application development platform (PaaS)
- GigaSpaces - middleware for the cloud, "cloudware"
- Google AppEngine - (PaaS)Now support python
- Heroku - Ruby on Rails in their Cloud
- Qrimp - An AJAX based PaaS
- RightScale - RightScale provides a platform and expertise that enable companies to create scalable web applications running on Amazon’s Web Services that are reliable, easy to manage, and cost less
基於雲計算的服務(Saas,雲存儲):
- CAM Solutions - SaaS Provider. Cloud Event Management, Autonomics and Monitoring-as-a-Service(TM)
- CloudStatus- CloudEnabler. Real-time performance trending of cloud infrastructure (currently AWS).
- Kaavo's IMOD is an easy to use online application. Cloud Computing Made Easy.
- Microsoft Mesh
- Nasstar - SaaS provider. Business grade Hosted Desktop service, UK market leaders.
- Nirvanix - Cloud Storage
- TrustSaaS - uptime monitoring and alerting service ('SaaS Weather Report') for Software as a Service (SaaS) run by an independent third party.
雲計算開源項目[1]
Enomalism, convirt, redhat genome, hyperVM, lxlabs, LN, OpenNEbula, reservoir-fp7, scalr,eucalyptus,ganeti,gplhost,ovirt。
Useful open source projects to build cloud platform:
Kenso, hyperic, virt-P2V。
使用雲計算服務的風險[1]
- 優先訪問權風險(Privileged user access.)
- 管理許可權風險(Regulatory compliance.)
- 數據處所風險(Data location.)
- 數據隔離風險(Data segregation.)
- 數據恢復風險(Recovery.)
- 調查支持風險(Investigative support.)
- 長期發展風險(Long-term viability.)
雲計算12層模型[17]
下麵是Dell描述的雲計算模型:
解釋:
這是一個明顯學術化的模型圖,就像ISO七層網路模型,永遠只有參考意義。
相比而言,下麵這個示意圖更具有表現力:
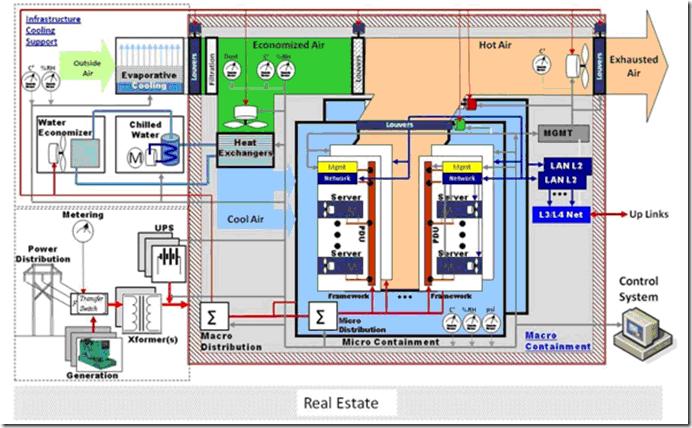
下麵是DELL描述的一個數據中心
事實上,這個數據中心和傳統的數據中心看起來沒有很大的不同,雲計算的含義是不能通過一個數據中心示意圖來表達的。
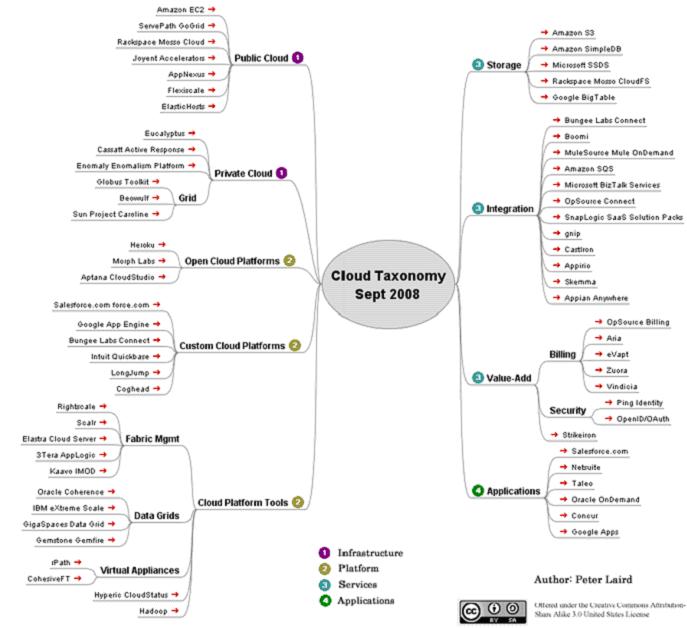
雲計算市場[18]
市場分為如下幾個層次:
- Cloud Computing
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Core Cloud Services
解釋如下:
- Infrastructure: the core computing resources and network fabric for the cloud deployment
- Platform: the software infrastructure that allows sys admins and developers to deploy an app to the cloud
- Core Services: additional services that can be woven into the cloud app, such as billing, storage, integration
- Applications: the ultimate cloud product - the actual cloud based application that the user touches. These number in the thousands.
市場視圖
下麵是市場參與者列表:
- Public Cloud
- Amazon EC2
- ServePath GoGrid
- Rackspace Mosso Cloud
- Joyent Accelerators
- AppNexus
- Flexiscale
- ElasticHosts
- Private Cloud
- Eucalyptus
- Cassatt Active Response
- Enomaly Enomalism Platform
- Grid
- Globus Toolkit
- Beowulf
- Sun Project Caroline
- Open Cloud Platforms
- Heroku
- Morph Labs
- Aptana CloudStudio
- Custom Cloud Platforms
- Salesforce.com force.com
- Google App Engine
- Bungee Labs Connect
- Intuit Quickbase
- LongJump
- Coghead
- Cloud Platform Tools
- Fabric Mgmt
- Rightscale
- Scalr
- Elastra Cloud Server
- 3Tera AppLogic
- Kaavo IMOD
- Data Grids
- Oracle Coherence
- IBM eXtreme Scale
- GigaSpaces Data Grid
- Gemstone Gemfire
- Virtual Appliances
- rPath
- CohesiveFT
- Hyperic CloudStatus
- Hadoop
- Fabric Mgmt
- Storage
- Amazon S3
- Amazon SimpleDB
- Microsoft SSDS
- Rackspace Mosso CloudFS
- Google BigTable
- Integration
- Bungee Labs Connect
- Boomi
- MuleSource Mule OnDemand
- Amazon SQS
- Microsoft BizTalk Services
- OpSource Connect
- SnapLogic SaaS Solution Packs
- gnip
- CastIron
- Appirio
- Skemma
- Appian Anywhere
- Value-Add
- Billing
- OpSource Billing
- Aria
- eVapt
- Zuora
- Vindicia
- Security
- Ping Identity
- OpenID/OAuth
- Strikeiron
- Billing
- Applications
- Salesforce.com
- Netsuite
- Taleo
- Oracle OnDemand
- Concur
- Google Apps [19]
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 劉黎明.雲計算
- ↑ What is cloud computing
- ↑ 雲計算如何實現隨用隨取(科技視點·用好用實高科技④).人民網-人民日報. 2019-11-25
- ↑ 張德厚.《與學界合作 Google推廣“雲運算技術”》,中廣新聞網,2008年1月30日.於2008年2月1日查閱
- ↑ 新浪科技.《戴爾在美申請“雲計算”商標》,新浪科技,2008年8月3日.
- ↑ http://gigaom.com/2008/02/28/how-cloud-utility-computing-are-different/
- ↑ Cloud vs. Utility Computing
- ↑ how cloud utility computing are different
- ↑ Distinguishing Cloud Computing from Utility Computing
- ↑ What is Cloud Computing?
- ↑ Wikipedia:Distributed computing
- ↑ [Different Flavors of Utility Computing (GRID vs. Cloud))
- ↑ Cloud Computing vs Grid Computing
- ↑ groups.google.com:Cloud Computing
- ↑ IBM:From Cloud Computing to the New Enterprise Data Center
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 wikipedia:Virtualization
- ↑ 劉黎明.雲計算12層模型
- ↑ 劉黎明.雲計算市場
- ↑ Visual Map of the Cloud Computing










雲計算是下一個時代的PC嗎?